How Digitalization is Changing Germany’s Automotive Manufacturing in 2025

Digitalization in the automotive Manufacturing industry is changing traditional business methods and improving the industry’s abilities. Businesses are creating linked systems and data-driven solutions that increase efficiency by combining modern technology with automotive engineering.
In the automotive manufacturing industry, digital transformation requires more than just implementing new technologies—it also includes reviewing processes, maximizing productivity, and adjusting to changing customer and market needs.
We’ll look at how digital transformation is impacting Germany’s automobile manufacturing industry in this blog. To provide a complete picture of the future of German automobile production, we will look closely at actual case studies, analyze the most recent data and statistics, and include statements from industry experts.
Digital transformation in automotive manufacturing helps manufacturers update their business processes, improve the supply chain, raise production, and increase passenger and vehicle safety. Automobile manufacturers may maintain their market dominance and attract in new business by implementing digital transformation.
Manufacturers have been able to increase electric vehicle production and fully embrace digital transformation due to the significant decline in battery prices.More investors are joining the trend of investing in electric vehicles as they gain popularity. By 2040, sales of electric cars are predicted by experts to surpass those of gasoline and diesel automobiles.
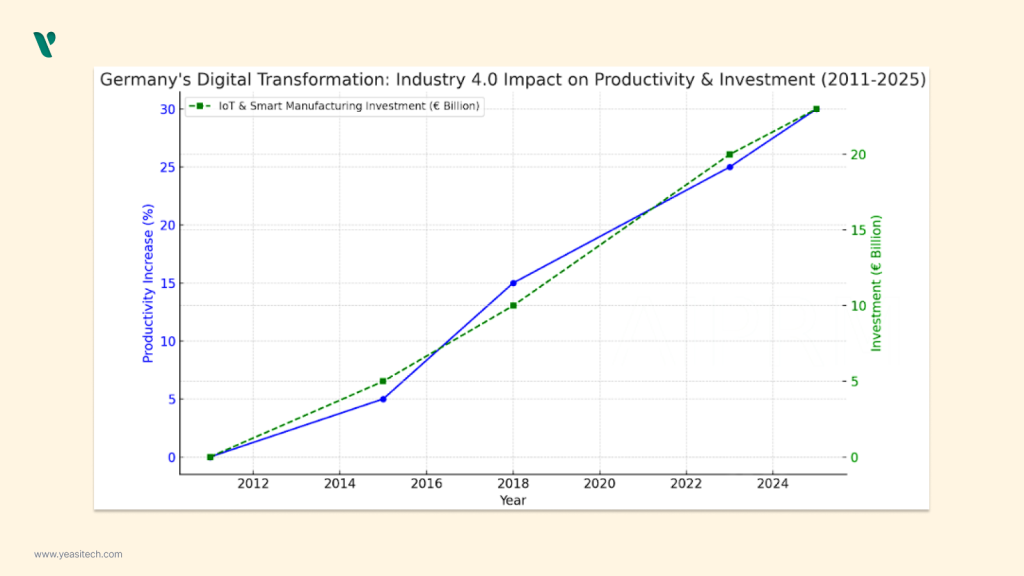
Germany, which has long been a leader in new technology, had a notable spike in digital transformation during the Fourth Industrial Revolution. In 2011, the German High-Tech Strategy introduced the concept of “industrial 4.0,” which promoted the idea of “smart factories,” or workplaces where people, machines, and systems collaborate well. German Automotive manufacturers have been steadily adopting modern digital technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), big data, and robotics over the last ten years.
According to a Roland Berger study, the implementation of Industry 4.0 is expected to result in a 30% rise in Germany’s overall industrial productivity by 2025 . 83% of German industrial firms have used Industry 4.0 technology in some capacity, according to the Fraunhofer Institute. 2023 expects Germany to invest more than €20 billion in IoT and smart manufacturing, primarily due to its thriving automotive manufacturing industry.
Lets look into the important technologies that are changing the automotive manufacturing industry:
Germany’s automotive manufacturing industry is evolving because of AI and ML, which lower costs, increase operational efficiency, and enable predictive maintenance. These technologies process large volumes of data from sensors on manufacturing lines to promptly optimize operations. Quality control is automated using AI, helping to identify flaws early in the production phase.
BMW’s AI-Driven Production BMW leads in applying AI to automotive manufacturing. At its Munich facility, AI systems continuously monitor the production process, identifying any issues that might lead to faults. According to BMW Group News, the corporation has increased efficiency by 20% and reduced production downtime by 25% as a result of AI. BMW uses AI for visual inspections, ensuring that each car meets strict requirements before leaving the plant, thus improving product quality.
“Artificial intelligence is revolutionizing automotive manufacturing by enabling greater precision, efficiency, and speed. We see it as a critical component of our future production strategy,”
– Oliver Zipse, CEO of BMW Group.
Germany has long been a leader in the automotive industry, which is one of the biggest users of industrial robots. Robots are essential to the car industry because they can do repetitive and difficult activities like welding, painting, and part assembly. Automation speeds up manufacturing overall, lowers human error, and improves product quality.
Automated Robotic Assembly by Audi : At its Ingolstadt, Germany facility, where more than 2,000 robots now collaborate with humans to create automobiles, Audi has completely incorporated robotics. These robots do very precise jobs like welding and part installation, and automated guided vehicles (AGVs) transport goods across the manufacturing facility. Audi MediaCenter reports that using advanced robotics has raised the production speed by 30% and reduced labor costs by 20%, helping Audi stay competitive while keeping quality high.
“Automation is key to scaling production without sacrificing quality. Our robotic systems allow us to create highly personalized vehicles with remarkable efficiency,”
– Peter Kössler, Board Member for Production and Logistics, Audi AG.
The Internet of Things (IoT) is helping German automakers create smart factories where machines are connected and talk to each other, allowing for quick decision-making. IoT sensors in manufacturing equipment gather data on how well they are working, making it possible to predict maintenance needs and reduce downtime.
Volkswagen’s Digital Production Network The Digital Production Platform (DPP), created in collaboration with Siemens, is Volkswagen’s means of integrating IoT into its production processes. Thousands of IoT sensors provide real-time data analysis, and the DPP connects more than 120 Volkswagen facilities worldwide, including those in Germany. Volkswagen can identify inefficiencies, reduce energy use, and increase manufacturing speed because of this. Volkswagen Newsroom reports that in 2021, the manufacturing efficiency of Volkswagen increased by 10% with the implementation of the DPP.
“IoT is essential for making our factories smarter, more efficient, and more sustainable. It allows us to integrate data across multiple plants and take actions in real time,”
– Oliver Blume, Chairman of Volkswagen Group.
German automakers are simulating and improving their production processes with digital twins, which are virtual copies of real products. These digital models let companies assess several production situations in a virtual environment before making changes to the real production line, which reduces risks and increases efficiency.
Siemens and BMW’s Digital Twin Partnership: Together, Siemens and BMW are using digital twin technology across all of their German manufacturing factories. By using digital twins, BMW may improve its processes and replicate different production scenarios without having to disrupt the real factory floor. According to Siemens Newsroom, this has led to a 20% decrease in costs and a 30% reduction in the time needed for production planning, helping BMW to introduce new models faster.
“Digital twins allow us to optimize production lines in real time, minimizing downtime and reducing costs. They are a critical component of our digital transformation strategy,” said Milan Nedeljković, Board Member for Production, BMW AG.
The following are the top five benefits that automotive manufacturers will experience as a result of their business and production processes going digital.
Retailers may reach a wider audience by establishing an online presence for automotive solutions. Most consumers these days shop online. Product exposure may be increased and business success can result from connecting with this vast audience using the appropriate tools and techniques. Keep in mind that 70% of automobile owners begin their car-buying journey online rather than at showrooms.
Automobile manufacturers are progressively upgrading the in-car experience for their customers by including infotainment and connection technologies into their cars. Nearly 90% of connected car customers are satisfied with features like voice-activated control, in-car internet access, smartphone applications, and virtual assistants.
Manufacturers may use real-time data monitoring and analysis into their business growth to improve resource usage and maximize production. Employee health risks associated with manufacturing may be reduced and machinery malfunctions can be avoided with the use of automotive digital transformation.
The more simple real-time data collecting procedure of fresh automated production systems increases the probability that manufacturers will detect any differences in quality throughout the manufacturing process. Massive financial losses and reclamations are also prevented by these techniques.
Large dataset analysis tools enable companies to identify trends and patterns. They may anticipate shifts in demand, better manage inventories, and improve production scheduling with predictive analytics, which lowers the possibility of having too much or too little stock. As a result, the production process runs more smoothly and accurately.
AI-powered supplier quality monitoring in supply chains is another way that digital transformation can improve them. Audi, Porsche, and Volkswagen, for example, utilize AI to search public news sources in more than 50 languages and determine if suppliers violate sustainability regulations in order to select the most suitable partners.
Automotive manufacturing in Germany has both possibilities and problems as a result of digital transformation. Upskilling the workforce is a must since automation demands that humans acquire some new abilities in order to interact with robots and AI.
Industrial networks are increasingly interconnected, making hacking more likely, therefore cybersecurity is also essential. To protect manufacturing lines, German automakers need to make significant investments in cybersecurity.
Despite these hurdles, the future of automotive manufacturing in Germany is clearly digital. The country’s focus on innovation and robust industrial base positions it to lead the next wave of transformation in the global automotive sector.
In conclusion, digitalization is changing the automotive manufacturing scene in Germany by improving efficiency, innovation, and security like never before. As the industry adopts new technologies such as AI, robotics, and strong cybersecurity, it sets itself up for future growth and leadership in the global market.
Companies like YeasiTech are leading this change, offering solutions that help manufacturers manage the challenges of digitalization and improve their operations. The automobile industry in Germany is set for a prosperous and competitive future because to these developments.
In order to increase productivity, quality, and sustainability in the production of vehicles, digitalization involves introducing digital technologies such as IoT, AI, automation, and data analytics into the automotive industry.
Through the use of data analytics to optimize the use of materials and energy, digitalization improves sustainability. Furthermore, it drives improvements in the creation of sustainable methods and electric vehicles.
Browse through the technical knowledge about latest trends and technologies our experienced team would like to share with you