Web Apps vs. Native Apps: Which is Best for Your MVP Startup in 2025?

In 2025, developing an MVP startup requires not just an innovative idea but also effectiveness, speed, and a user-centered methodology. When creating your Minimum Viable Product, one of the most important choices you’ll have to make is whether to design a web application or a native app.
Although each method offers benefits of its own, the optimal one for you will rely on your goals, target market, and available resources. In order to determine which web app or native app would be the best choice for your MVP startup in 2025, this post will look at the benefits and drawbacks of each.
Let’s define an MVP before diving into details of app development. A minimum viable product, or MVP, is a basic version of your product with only enough functionality to attract beta testers and validate your concept.
The main goal is to gather feedback to make improvements before going all in on development. It’s important to move quickly and keep costs down. In fact, CB Insights reports that 29% of startups fail because they run out of money, often due to long and expensive development processes.
If you want to know why MVP Development is Crucial for Startup Success for 2025. Read HERE
Here are the top 5 differences between Web Apps and native apps. This comparison will help you choose the right app for your business and make your decision easier:
| Parameters | Native App | Web Apps |
| App Store Distribution | Native apps are available through app stores specific to each platform, such as the Apple App Store or Google Play Store. Users need to download and install the apps from these stores to use them. | Web Apps don’t need to be distributed through app stores. You can download and install them without needing an app store. |
| Platform Compatibility | Developers use unique programming languages and tools for each platform to build native apps, such as Swift for iOS and Java for Android. | You can install web apps on computers, tablets, and smartphones that function and look like native programs. |
| Cost | Native apps are designed for specific platforms like iOS or Android. This means developers have to create them twice, once for each platform. | Web app development is cheaper than developing native apps. Web Apps use web technologies, allowing developers to use one codebase for many platforms. |
| Access to Native APIs | Native apps can easily connect with different device features, like push notifications, camera access, contacts, and more. | Web Apps have limited access to device APIs and features. |
| Offline Functionality | Native programs have many offline features. Users can access and use the app’s features and content without an internet connection because they can save data directly on their device. | Web apps can work offline because of service workers and caching. They can save data and resources on your device, so you can use the app even without an internet connection or in places with weak signals. |
Let’s discuss advantages of Native Apps for MVP Startup in detail:

Native apps function more quickly and offer a more seamless user experience since they are created especially for the platforms on which they are intended. Native apps are frequently the greatest choice for Minimum viable products (MVPs) that require rapid reactions and quickness, such as gaming apps or ride-sharing services with real-time updates.
Uber initially started with a native app MVP to take full advantage of the phone’s GPS and notification system for real-time ride-hailing. Their decision to prioritize performance paid off, rapidly scaling the platform from a local to a global service.
Native apps can function without an internet connection, making them the preferred choice for MVPs where constant connectivity can’t be assumed, like in rural areas or regions with unstable networks.
The GPS, microphone, and camera of a device are all fully accessible to native apps. This access allows them to provide advanced features that web apps can’t. For MVP startups looking to develop apps for fields like advanced data analytics, augmented reality, or the Internet of Things, this is especially essential.
A report from Business of Apps says that people spend 90% of their mobile time using apps. This shows why it’s important to make apps interesting and full of useful features that people enjoy using.
Push notifications, which can greatly enhance user engagement, are easier to implement on native apps. Direct engagement with users promotes improved retention rates, which are essential for early growth for an MVP business.
“When it comes to delivering rich, complex user experiences, native apps are still king.” — Benedict Evans, Mobile Analyst
Let us read about possible challenges of Native Apps:
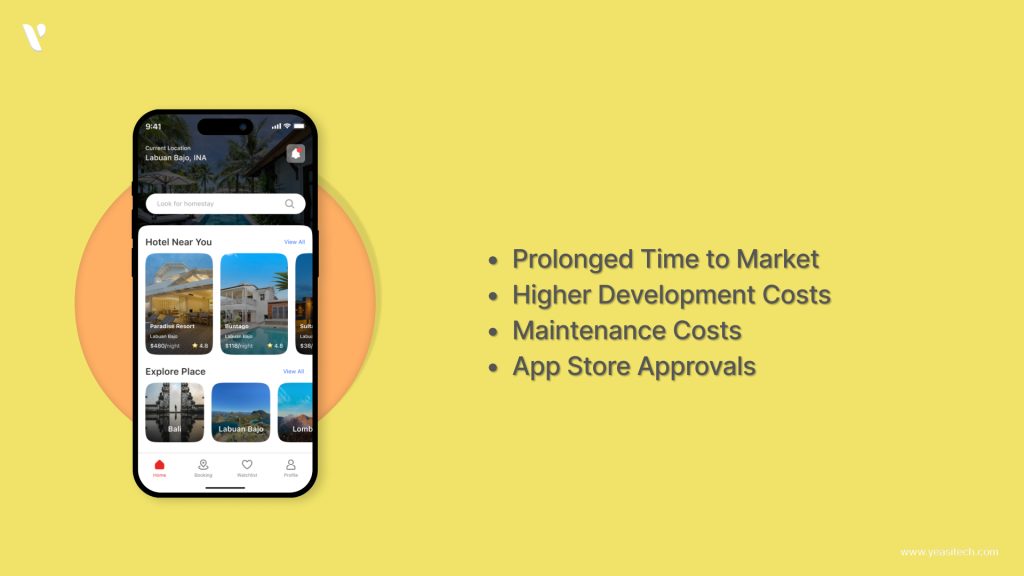
Building native apps takes more time because you have to write, test, and fix the code separately for each platform (like iOS and Android). This can slow down your launch and make it longer to get your app to users.
Each device type, such as iPhones and Android phones, needs a different native app to be developed. This takes twice as much time and money. For a new startup trying to launch a basic version of their app, this can be a big financial challenge.
You must release fresh versions of your software and make sure it is compatible with the most recent system changes after it has been released. Compared to online apps, which simply require server updates, this may end up costing more in the long run.
It can take a while for your software to be allowed by Google Play or the App Store due to their strict policies. For entrepreneurs hoping for a speedy launch, these delays can be an issue.
Let us read about the advantages of Web Apps for MVP Startup in detail:

Search engines have the ability to index web apps, which opens up the possibility of natural discovery. This is a strong point for MVP startups aiming to grow their audience quickly through content marketing and SEO strategies.
“Web apps are perfect for reaching users quickly and iterating without the roadblocks posed by app store approvals or platform dependencies.” — Sarah Perez, TechCrunch
For a web-based app to work on any device with a browser, including desktop computers and smartphones, separate versions for iOS, Android, or other platforms are not necessary. This helps startups greatly by saving money and time on development.
The fact that there will be more than 4.3 billion mobile internet users worldwide by 2025, according to Statista, highlights the extensive reach that a web app may offer.
Updates and modifications take effect immediately without requiring the user to download a new version of the program because it runs on a server. For a minimum viable product (MVP), this is crucial when you’re iteratively improving it in response to user input.
Generally speaking, creating web apps is less expensive than creating native apps for various platforms. For an MVP startup, this can mean a faster launch with a smaller budget. The cost difference is significant.
Web apps typically cost between $5,000 and $20,000, depending on complexity, whereas native apps can cost anywhere from $30,000 to $100,000.
Let us read about possible challenges of Web Apps:

Web apps are usually slower and less responsive than native apps. This can affect how users experience the app, especially in cases where a lot of processing power or large amounts of data are needed.
Web apps lack access to many device-specific features, such as camera controls, offline functionality, push notifications, and deep system integration. This can limit the functionality of your MVP, particularly if your product relies on hardware capabilities.
Web apps in general are still not as dependable when there is no internet, even though Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) have made progress in providing offline functionality. This can be a restriction based on who your target market is and how your product is used.
Let’s look into a Real-Life inspiring story that can inspire you and give you a clear idea about what app to choose for your MVP startup:
Spotify started out as a desktop program but has now developed into a web application as well as a dedicated mobile app.
WhatsApp began as a straightforward chat service and was first made available as a native iOS and Android app.
Originally designed as web apps, Trello is a project management solution emphasizing ease of use and teamwork.
The key consideration of choosing a Native app for MVP Startup:
The key consideration of choosing Web Apps:
The platform you choose to build your app will determine its success and your MVP Startup. Therefore, it is essential to choose the appropriate app by taking into account all factors, demands, and specifications related to your business and users. In this blog, we have discussed the comprehensive difference between Web App V/S Native. We discussed the pros and cons, features, and real life case studies.
However, if you are still not able to decide whether you need a Web App or native app, YeasiTech is here to help you. You can choose the ideal platform for your apps with the help of our expert group of app developers. They will determine the best course of action after assessing your needs.
Contact our professionals and receive proven technological answers to your questions.
A web app is used through a browser and works on different devices, while a native app is downloaded and installed on a device, giving better performance and access to certain features of the device.
A web app is generally more cost-effective, as it allows you to reach users on multiple platforms without developing separate versions for different operating systems.
If your target audience spends the majority of their time on mobile applications, like those for gaming or fitness, or if your MVP Startup depends heavily on device-specific capabilities like the camera, GPS, or push notifications, then a native app is the best option.
Choose native apps for better performance, offline access, and device integration, but with higher development costs. Opt for web apps for cross-platform compatibility, easier updates, and lower costs, but with limited offline functionality. The choice depends on budget, user experience needs, and target audience.
Choose native apps for better performance, security, and platform-specific user experience, but expect higher development costs. Opt for hybrid apps for faster, cost-effective cross-platform development, though they may sacrifice performance and deep OS integrations.
Pick a PWA for cross-platform reach and cost efficiency or a Native App for better performance and deeper device integration—choose based on your priorities.
YeasiTech is a trusted IT service partner with 8+ years of experience, empowering 250+ businesses with scalable web, mobile and AI solutions.
Explore related topics to broaden your understanding and gain actionable insights that can transform your strategies.